boundaries
Type of resources
Topics
Keywords
Contact for the resource
Provided by
Years
Formats
Representation types
Update frequencies
status
-
The rationale for developing this product was the recognized need for a standard and adaptable marine grid that could be used for planning or analysis purposes across projects. This nested grid has five spatial resolutions: 8km, 4km, 2km, 1km, and 500m. It covers the extent of the EEZ on the Canadian Pacific coast, and further east in order to encompass the Fraser River Delta and Puget Sound to account for ecological importance. There is a step-by-step methods document that gives users information on how to recreate the grid with ArcMap.
-
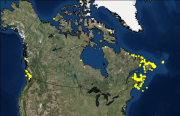
Canada has the longest coastline in the world, measuring 243,790 kilometers. Many of our waterways along the coastline have to be dredged regularly to keep shipping channels and harbours open and safe for navigation; and this material is sometimes best disposed of at sea. Schedule 5 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (CEPA) defines an exclusive list of materials and substances suitable for disposal at sea in Canada, which is in accordance with the London Protocol (1996). They are: dredged material, fish waste resulting from industrial fish processing operations, ships or platforms, inert and inorganic geological matter, uncontaminated organic matter of natural origin, and bulky substances. The disposal of any substance into the sea, on the seabed, in the subsoil of the seabed, or onto ice, from a ship, an aircraft, a platform or other structure is not allowed unless a permit is issued by the Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) Disposal at Sea Program. Incineration at sea, as well as importing or exporting a substance for disposal at sea is also prohibited. More information on Disposal at Sea is available at: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/disposal-at-sea.html The Active and Inactive Disposal at Sea Sites in Canadian Waters dataset provides spatial and related information of at-sea disposal sites approved for use in Canada in the last ten years and that remain open for consideration for additional use. Any additional use of a disposal site must be conducted in accordance with the terms and conditions of a valid Disposal at Sea permit. The dataset may be of use in relation to Disposal at Sea permit applications. For some Disposal at Sea permit applications the data may be of use in assessing serious harm to fish under the Fisheries Act and assessing interference with navigation under the Navigation Protection Act.
-
The Canadian Environmental Sustainability Indicators (CESI) program provides data and information to track Canada's performance on key environmental sustainability issues. The Global trends in protected areas indicator reports on global terrestrial and marine area afforded protection for the conservation of nature. The indicator also shows a comparison of area protected among 10 selected countries. Global information on protected areas is collected, analyzed and made available by the World Database on Protected Areas. Information is provided to Canadians in a number of formats including: static and interactive maps, charts and graphs, HTML and CSV data tables and downloadable reports. See the supplementary documentation for the data sources and details on how the data were collected and how the indicator was calculated.
-
The Canadian Environmental Sustainability Indicators (CESI) program provides data and information to track Canada's performance on key environmental sustainability issues. The Global trends in protected areas indicator reports on global terrestrial and marine area afforded protection for the conservation of nature. The indicator also shows a comparison of area protected among 10 selected countries. Global information on protected areas is collected, analyzed and made available by the World Database on Protected Areas. Information is provided to Canadians in a number of formats including: static and interactive maps, charts and graphs, HTML and CSV data tables and downloadable reports. See the supplementary documentation for the data sources and details on how the data were collected and how the indicator was calculated.
-
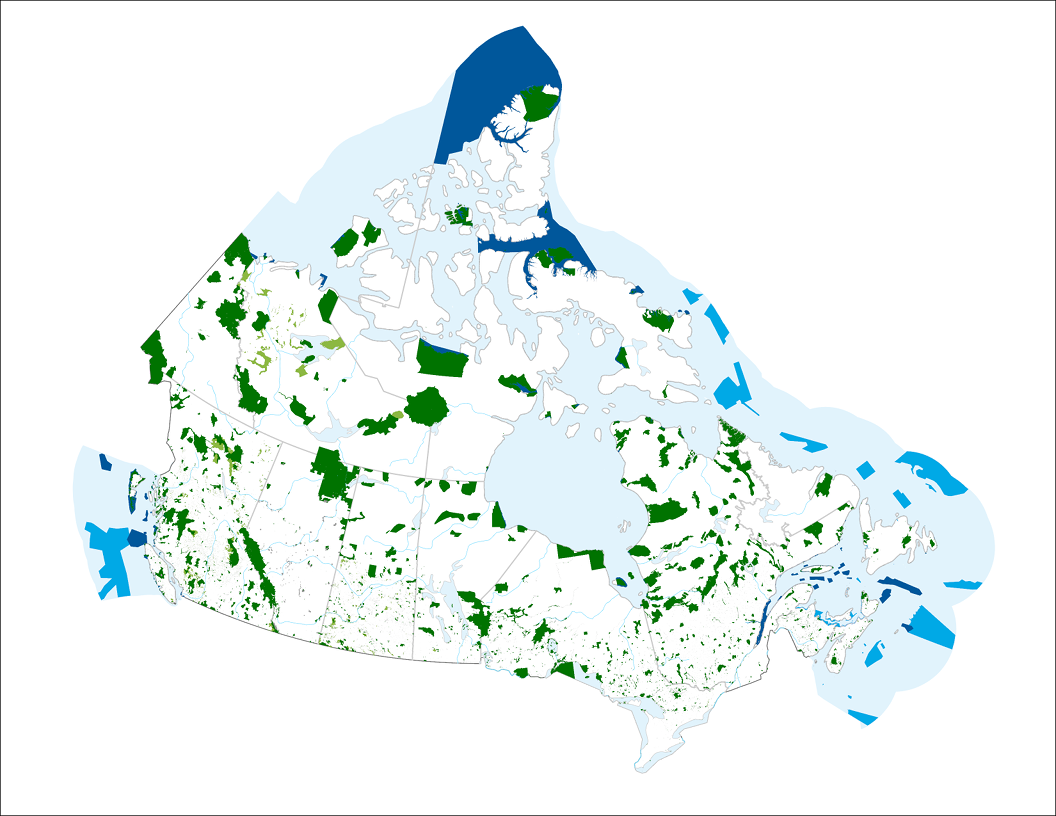
The Canadian Protected and Conserved Areas Database (CPCAD) is the authoritative source of data on protected and conserved areas in Canada. The database consists of the most up-to-date spatial and attribute data on marine and terrestrial protected areas in all governance categories recognized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), as well as other effective area-based conservation measures (OECMs, or conserved areas) across the country. Indigenous Protected and Conserved Areas (IPCAs) are also included if they are recognized as protected or conserved areas. CPCAD adheres to national reporting standards and is available to the public. The CPCAD is compiled and managed by Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC), in collaboration with federal, provincial, territorial, and other reporting authorities that provide the data. The database contains combined data from all these Canadian reporting authorities, who have determined that their areas meet the Canadian criteria as protected or conserved areas. The CPCAD is used by a wide range of organizations, including governments, environmental non-governmental organizations (ENGOs), academia, land managers, industry, and the general public. CPCAD supports many uses including Canada’s national reporting on protected areas, Canada’s international reporting on protected areas as a result of Canada’s commitments under the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity, and Canada’s protected areas program by providing baseline information. More detailed information on CPCAD is available by downloading the User Manual. The data is current as of the date of the most recent revision.
-
The Canadian Environmental Sustainability Indicators (CESI) program provides data and information to track Canada's performance on key environmental sustainability issues. The Extent of Canada's wetlands indicator is a measure of the extent of Canadian wetlands, and provides a baseline from which change can be measured. A wetland is defined as a land that is saturated with water long enough to promote aquatic processes as indicated by poorly drained soils, hydrophytic vegetation and various kinds of biological activity which are adapted to a wet environment. Information is provided to Canadians in a number of formats including: static and interactive maps, charts and graphs, HTML and CSV data tables and downloadable reports. See the supplementary documentation for data sources and details on how those data were collected and how the indicator was calculated.
-
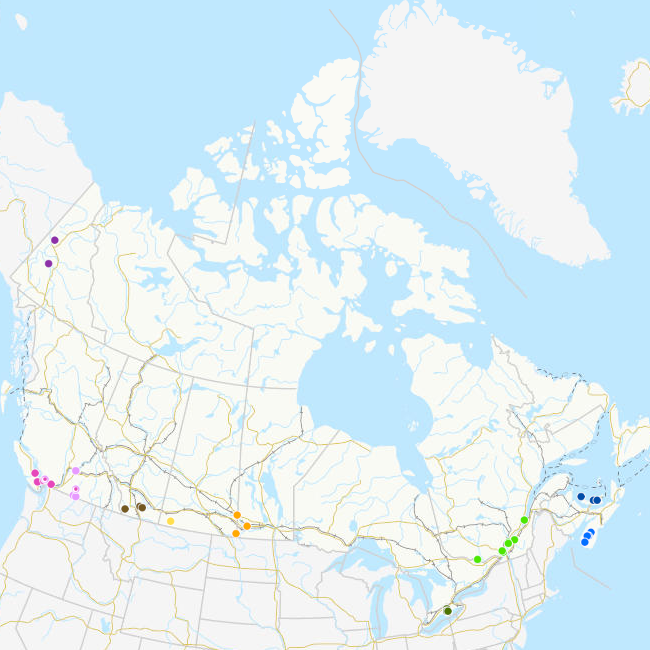
A Priority Place is an area of high biodiversity value that is seen as a distinct place with a common ecological theme by the people who live and work there. As part of the Pan-Canadian approach to transforming species at risk conservation in Canada, a total of 11 Priority Places were affirmed by federal, provincial, and territorial governments in December 2018. The places selected have significant biodiversity, concentrations of species at risk, and opportunities to advance conservation efforts. In each Priority Place, the federal and provincial or territorial governments are working with Indigenous Peoples, partners, and stakeholders to develop conservation implementation plans. This dataset captures a small sample of the projects that are underway in these Priority Places. Over time, it will be expanded to include more projects. Some projects span various areas of a Priority Place but are reflected in this dataset as a single center point. This dataset is not to be used for legal purposes.
-
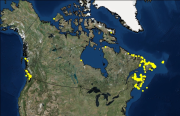
Canada has the longest coastline in the world, measuring 243,790 kilometers. Many of our waterways along the coastline have to be dredged regularly to keep shipping channels and harbours open and safe for navigation; and this material is sometimes best disposed of at sea. Schedule 5 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (CEPA) defines an exclusive list of materials and substances suitable for disposal at sea in Canada, which is in accordance with the London Protocol (1996). They are: dredged material, fish waste resulting from industrial fish processing operations, ships or platforms, inert and inorganic geological matter, uncontaminated organic matter of natural origin, and bulky substances. The disposal of any substance into the sea, on the seabed, in the subsoil of the seabed, or onto ice, from a ship, an aircraft, a platform or other structure is not allowed unless a permit is issued by the Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) Disposal at Sea Program. Incineration at sea, as well as importing or exporting a substance for disposal at sea is also prohibited. More information on Disposal at Sea is available at: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/disposal-at-sea.html The Active and Inactive Disposal at Sea Sites in Canadian Waters dataset provides spatial and related information of at-sea disposal sites approved for use in Canada in the last ten years and that remain open for consideration for additional use. Any additional use of a disposal site must be conducted in accordance with the terms and conditions of a valid Disposal at Sea permit. The dataset may be of use in relation to Disposal at Sea permit applications. For some Disposal at Sea permit applications the data may be of use in assessing serious harm to fish under the Fisheries Act and assessing interference with navigation under the Navigation Protection Act.
-
Canada has the longest coastline in the world, measuring 243,790 kilometers. Many of our waterways along the coastline have to be dredged regularly to keep shipping channels and harbours open and safe for navigation; and this material is sometimes best disposed of at sea. Schedule 5 of the Canadian Environmental Protection Act, 1999 (CEPA) defines an exclusive list of materials and substances suitable for disposal at sea in Canada, which is in accordance with the London Protocol (1996). They are: dredged material, fish waste resulting from industrial fish processing operations, ships or platforms, inert and inorganic geological matter, uncontaminated organic matter of natural origin, and bulky substances. The disposal of any substance into the sea, on the seabed, in the subsoil of the seabed, or onto ice, from a ship, an aircraft, a platform or other structure is not allowed unless a permit is issued by the Environment and Climate Change Canada (ECCC) Disposal at Sea Program. Incineration at sea, as well as importing or exporting a substance for disposal at sea is also prohibited. More information on Disposal at Sea is available at: https://www.canada.ca/en/environment-climate-change/services/disposal-at-sea.html The Active Disposal at Sea Sites in Canadian Waters dataset provides spatial and related information of at-sea disposal sites approved for use in Canada in the last ten years. Any additional use of a disposal site must be conducted in accordance with the terms and conditions of a valid Disposal at Sea permit. The dataset may be of use in relation to Disposal at Sea permit applications. For some Disposal at Sea permit applications the data may be of use in assessing serious harm to fish under the Fisheries Act and assessing interference with navigation under the Navigation Protection Act.
-
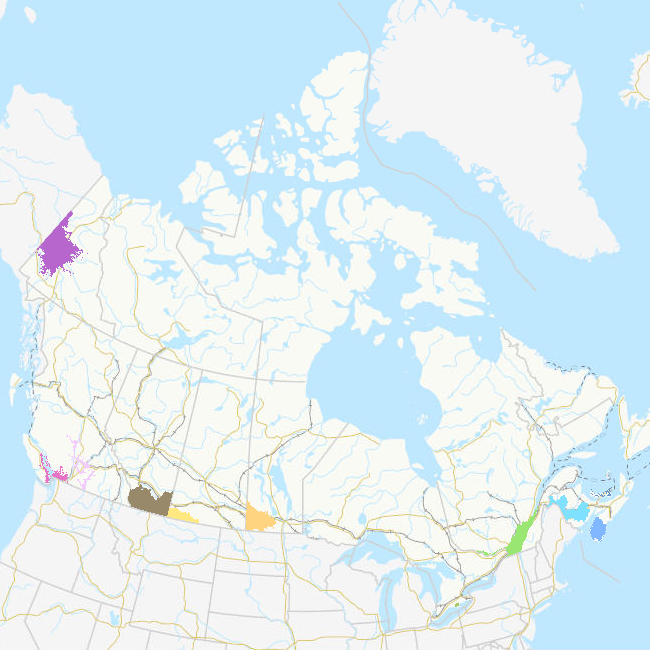
A Priority Place is an area of high biodiversity value that is seen as a distinct place with a common ecological theme by the people who live and work there. As part of the Pan-Canadian approach to transforming Species at Risk conservation in Canada, a total of 11 Priority Places were affirmed by federal, provincial, and territorial governments in December 2018. The places selected have significant biodiversity, concentrations of species at risk, and opportunities to advance conservation efforts. In each Priority Place, the federal and provincial or territorial governments are working with Indigenous Peoples, partners, and stakeholders to develop conservation implementation plans. This dataset displays the geographic area covered by each of the 11 Priority Places using the best available information from the Canadian Wildlife Service (CWS). Boundary information for each Priority Place was provided by its respective CWS regional office. The federal government, in collaboration with the provinces and territories, has agreed to the implementation of the Pan-Canadian Approach to Transforming Species at Risk Conservation in Canada. This new approach shifts from a single-species approach to conservation to one that focuses on multiple species and ecosystems. This enables conservation partners to work together to achieve better outcomes for species at risk. These 11 Priority Places are complemented by a suite of Community-Nominated Priority Places (CNPP), identified through an open call for applications.
